
is arithmetic, because each step subtracts 4. is arithmetic, because each step adds three and 7, 3, 1, 5. An arithmetic sequence goes from one term to the next by always adding (or subtracting) the same value. Arithmetic sequences consist of consecutive terms with a constant difference, whereas geometric sequences consist of consecutive terms in a constant ratio. The two simplest sequences to work with are arithmetic and geometric sequences. The differences between the two sequence types depend on whether they are arithmetic or geometric in nature. To this end, an Arithmetic and Geometric approach are integral to such a calculation, being two sure methods of producing pattern-following sequences and demonstrating how patterns come to work. The terms consist of an ordered group of numbers or events that, being presented in a definite order, produce a sequence. Use the "Calculate" button to produce the results. For each sequence, state if it is arithmetic, geometric, or neither.
Arithmetic and geometric sequences and series series#
When a series of numbers are arranged in a specific pattern, we call it a.

A geometric sequence has a constant ratio between each pair of consecutive terms. Geometric sequence Fibonacci sequence Harmonic sequence. This is similar to the linear functions that have the form y m x + b. An arithmetic sequence has a constant difference between each consecutive pair of terms. Formulas for the Nth Term: Recursive and Explicit Rules To determine any number within a geometric sequence, there are two formulas that can be utilized. Insert common difference / common ratio value Two common types of mathematical sequences are arithmetic sequences and geometric sequences. where n is any positive integer greater than 1.Insert the n-th term value of the sequence (first or any other).An example is: 2,4,8,16,32, So to find the next term in the sequence we would. Use the dropdown menu to choose the sequence you require A geometric sequence has a constant ratio (multiplier) between each term.If this sequence is geometric, continue it.By applying this calculator for Arithmetic & Geometric Sequences, the n-th term and the sum of the first n terms in a sequence can be accurately obtained. If this sequence is arithmetic, continue it. geometric from a story problem.ĭice – Have students generate their own sequences somehow. Word Problem Practice – Put more word problems and their worked solutions in our notebooks! Students seem to struggle with determining arithmetic vs. Solve Two Ways – Make a notebook page where students have to solve for a certain term or sum recursively AND using the formula. Fix this!Īrithmetic vs Geometric Card Sort – Students must determine whether to solve for r or d!
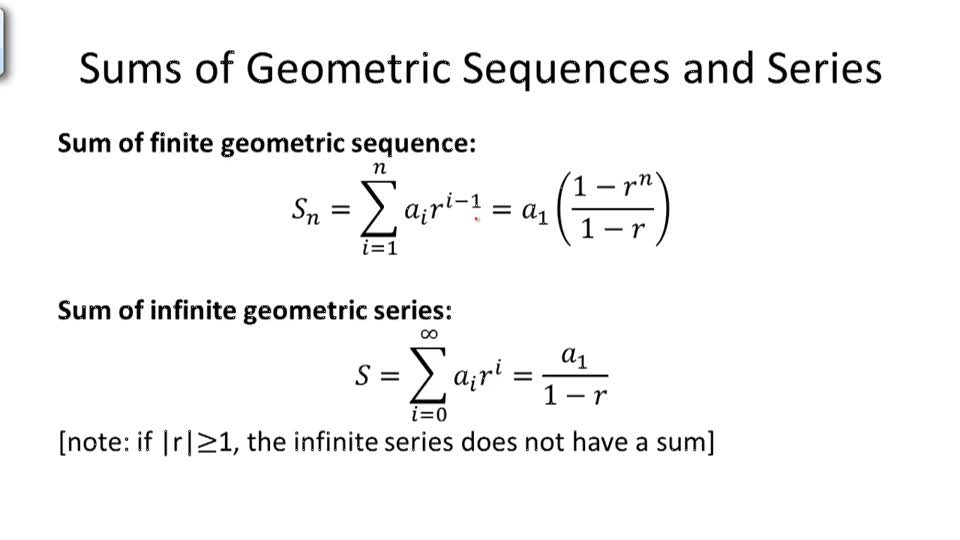
Sequence vs Series Card Sort – Some students seem to confuse the definition of series with the definition of arithmetic. A geometric sequence has the form a, ar, ar2. Now, I need to get my kiddos to see the need for the formula. Show that 12 is not a term of the arithmetic sequence 210, 197, 184. I think this is definitely worth considering! I see the need for the formula. Steps to Find the Sum of an Arithmetic Geometric Series. Calculate the sum of an infinite geometric series when it exists. Geometric: ¾, 3, 12, 48, 192, a 1 ¾ common ratio 4 Recursive Definition (Formula) of a Sequence In order to describe a sequence to someone, we simply must tell them where to start, and then how. A couple of students suggested that I spend more time having them find values recursively before I ever give them formulas. Calculate the nth partial sum of a geometric sequence. Geometric Sequences Geometric Sequences are built by repeatedly multiplying the same number (called the common ratio) to the first term a 1.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
